|
Latest Research Highlights |
Dynamic Reconfiguration of GCM components CoreGRID Technical Report TR-0173 [pdf]: We detail in this report past research and current/future developments in formal specification of Grid component systems by temporal logic and consequent resolution technique, for an automated dynamic reconfiguration of components. It is analysed the specification procedure of GCM (Grid Component Model) components and infrastructure in respect to their state behaviour, and the verification process in a dynamic and reconfigurable distributed system. Furthermore it is demonstrated how an automata based method is used to achieve the specification, as well as how the enrichment of the temporal specification language of Computation Tree Logic CTL with the ability to capture norms, allows to formally define the concept of reconfiguration. | 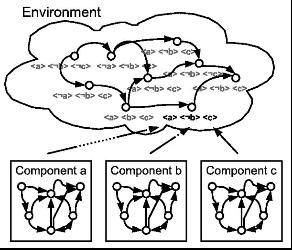
| Towards a Spatio-Temporal sKeleton Model Implementation on top of SCA CoreGRID Technical Report TR-0171 [pdf]:
This report investigates an implementation of STKM, a Spatio-Temporal sKeletonModel. STKM expands the Grid Component Model (GCM) with an innovative programmable approach to compose an application by combining component, workflow and skeleton concepts. We explore a projection of the model on top of SCA and its implementation using Tuscany Java SCA. Experimental results show the need and benefits of the high level of abstraction offered by STKM. | 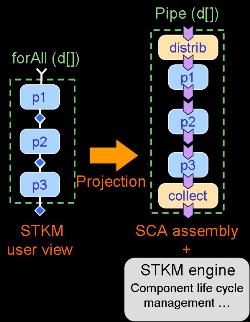
| A Scheduler for a Multi-paradigm Grid Environment CoreGRID Technical Report TR-0155 [pdf]: Typical Grid environments are characterized by a two-level scheduling: super and local scheduling. While the former regards the selection of proper resources to execute high level tasks, the latter regards the scheduling of tasks to processors for optimizing performance and hardware exploitation. This paper proposes a super scheduler that provides services to domain specific high-level programming environments, while taking advantage of middleware libraries to handle the complexity of Grid computing. To prove the flexibility of the scheduler, three different programming environments with slightly different programming abstractions have been integrated with it: a problem solving environment (SEGL), a skeleton framework (Calcium) and a workflow enactment engine (SAWE). The integration above shows how it is possible to facilitate the adoption of the ProActive middleware for the development of complex Grid applications. | 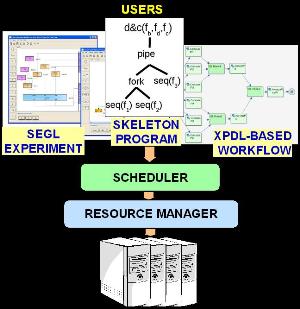
|
|
|
Last Updated ( Wednesday, 24 September 2008 )
|